Introduction
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are constantly seeking ways to build scalable, efficient, and secure applications. The combination of serverless architecture and robust database solutions offers a powerful approach to meeting these needs. This article will guide you through the process of building a secure serverless application using AWS services and MongoDB Atlas, focusing on the critical aspects of security and connectivity. AWS Lambda, a cornerstone of serverless architecture on the AWS platform, enables you to run code without provisioning or managing servers. When paired with MongoDB Atlas, a fully managed cloud database service, you can create highly scalable and flexible applications that can handle varying workloads efficiently.
Configuring Your Development Environment
Before diving into the application build, it's crucial to set up a proper development environment. AWS Cloud9 provides an excellent integrated development environment (IDE) that's particularly well-suited for serverless development.
To get started with Cloud9:
- Log into your AWS Console and navigate to the Cloud9 service.
- Click "Create environment" and follow the prompts to set up your IDE.
- Once created, you'll have a fully functional development environment in your browser.
Building the Application: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Initialize the SAM Project
First, we'll use the SAM CLI to initialize a new project:
sam init --runtime python3.8 --dependency-manager pip --app-template hello-world --name my-serverless-app
Step 2: Modify the SAM Template
Next, we'll modify the template.yaml file to include our MongoDB Atlas connection. Here's an example of how you might structure this:
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Transform: AWS::Serverless-2016-10-31
Description: Serverless API with MongoDB Atlas
Resources:
MyFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
Handler: app.lambda_handler
Runtime: python3.8
Environment:
Variables:
MONGODB_URI: !Ref MongoDBAtlasURI
Events:
Api:
Type: Api
Properties:
Path: /items
Method: post
Parameters:
MongoDBAtlasURI:
Type: String
Description: MongoDB Atlas connection string
Step 3: Implement the Lambda Function
Now, let's implement our Lambda function in app.py:
import json
import os
from pymongo import MongoClient
def lambda_handler(event, context):
client = MongoClient(os.environ['MONGODB_URI'])
db = client.myDatabase
collection = db.myCollection
body = json.loads(event['body'])
result = collection.insert_one(body)
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps({'id': str(result.inserted_id)})
}
This function connects to MongoDB Atlas, inserts a document based on the API request body, and returns the inserted document's ID.
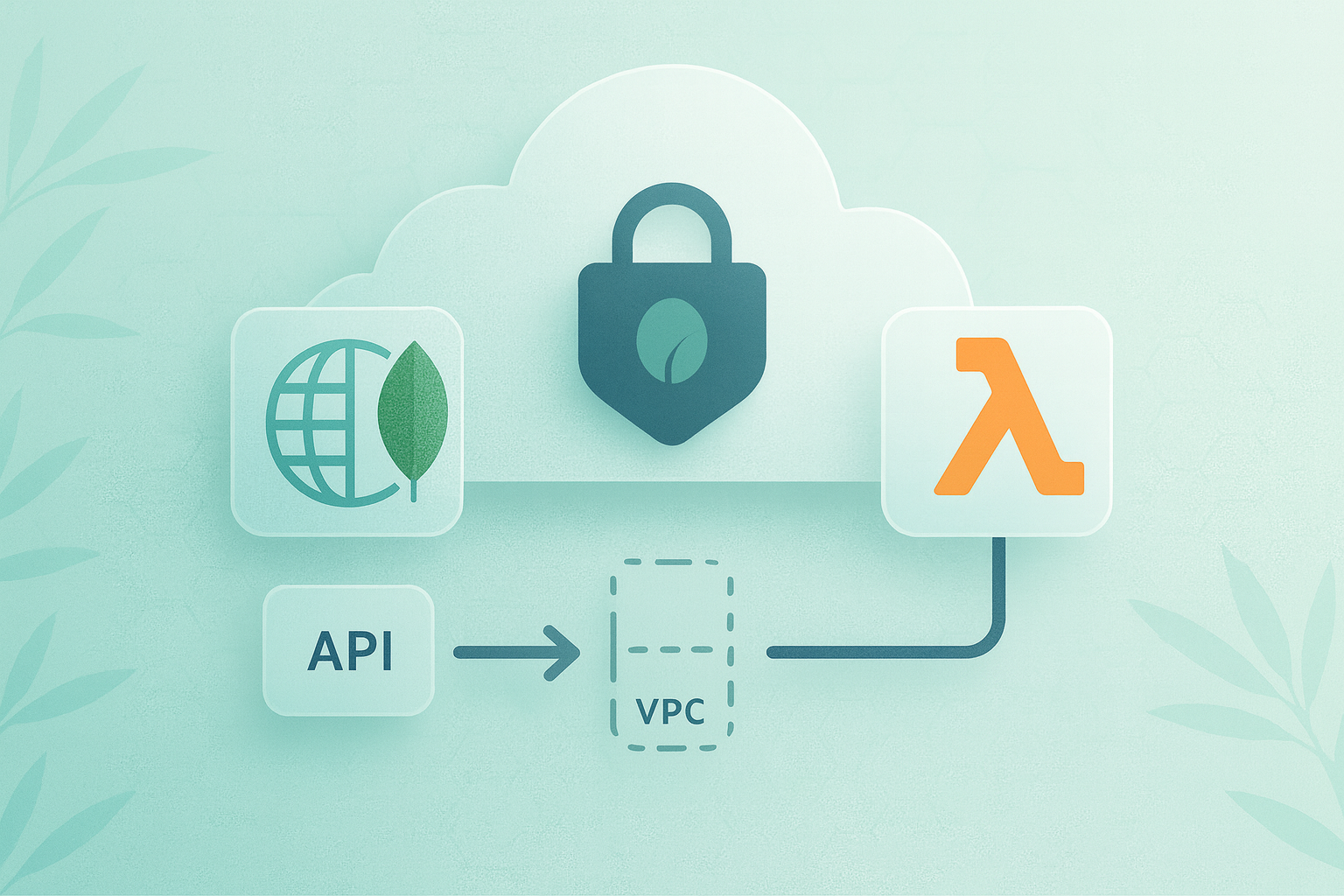
Ensuring Secure Connectivity with MongoDB Atlas
Security is important when connecting your serverless application to a database. We'll use VPC peering to establish a secure connection between your AWS VPC and MongoDB Atlas VPC.
Setting Up VPC Peering
- In the MongoDB Atlas console, navigate to Network Access > Peering.
- Click "Add Peering Connection" and select AWS as the cloud provider.
- Enter your AWS account ID and VPC ID.
- Copy the peering connection ID provided by Atlas.
Now, in the AWS Console:
- Go to the VPC Dashboard and select "Peering Connections".
- Click "Create Peering Connection" and paste the ID from Atlas.
- Accept the peering request in your AWS account.
Finally, update the route tables in both AWS and MongoDB Atlas to allow traffic between the peered VPCs.
Testing and Validation
With our application built and secure connectivity established, it's time to test our serverless API.
- Deploy your application using sam deploy --guided.
- Once deployed, AWS SAM will provide you with an API Gateway endpoint URL.
- Use a tool like Postman or curl to send a POST request to your API:
curl -X POST https://your-api-gateway-url/items -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"name": "Test Item", "description": "This is a test item"}'
- Verify that the item was successfully inserted into your MongoDB Atlas database.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Effective monitoring is crucial for maintaining the health and performance of your serverless application. AWS provides several tools to help you monitor and troubleshoot your application:
- AWS CloudWatch: Use CloudWatch to set up logs, metrics, and alarms for your Lambda functions and API Gateway.
- X-Ray: Implement AWS X-Ray to trace requests as they travel through your application, helping you identify performance bottlenecks.
- MongoDB Atlas Monitoring: Utilize the built-in monitoring tools in MongoDB Atlas to track database performance and query patterns.
Best Practices for Serverless Security
To ensure the ongoing security of your serverless application:
- Use IAM roles and policies to implement the principle of least privilege.
- Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit.
- Regularly update your Lambda function's runtime and dependencies.
- Implement API Gateway authentication and authorization mechanisms.
- Use AWS Secrets Manager to securely store and rotate your MongoDB Atlas connection string.
Conclusion
By following these best practices and leveraging the security features of both AWS and MongoDB Atlas, you can build a robust, scalable, and secure serverless application that meets the demands of modern cloud-native architectures.